The United States of America boasts one of the world's largest and most influential economies, playing a central role in global trade, finance, and innovation. Understanding the intricacies of the USA's economy requires exploring its key components, historical evolution, and current dynamics. This comprehensive guide provides insights into the various aspects that shape the economic landscape of the United States.
1. Historical Foundations of the USA's Economy
From Agrarian Roots to Industrial Powerhouse
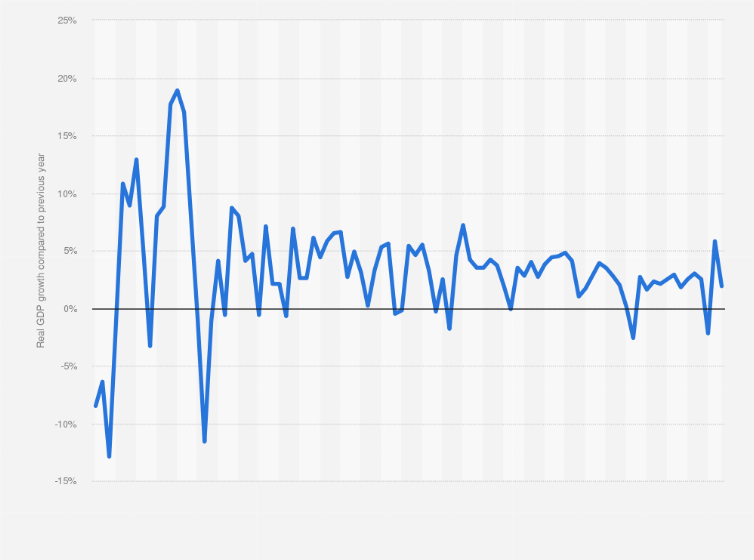
The USA's economic journey traces back to its agrarian beginnings, evolving into an industrial powerhouse during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Industrial Revolution propelled the nation into a period of rapid economic growth, laying the foundation for its emergence as a global economic leader.
2. Key Economic Indicators

Measuring the Pulse of the Economy
Several key indicators gauge the health of the USA's economy. These include Gross Domestic Product (GDP), unemployment rates, inflation rates, and consumer spending. These indicators provide valuable insights into economic growth, employment trends, and overall economic stability.
3. Sectoral Composition of the Economy

Diverse and Dynamic Sectors
The USA's economy is characterized by its diverse sectors, each contributing uniquely to its overall economic prowess. These sectors include manufacturing, services, agriculture, and technology. The services sector, encompassing finance, healthcare, and information technology, holds particular significance in the modern economy.
4. Global Trade and Economic Partnerships

International Influence and Trade Dynamics
The USA is a major player in global trade, engaging in economic partnerships with nations worldwide. Trade agreements, such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), shape the nation's trade policies and influence its economic relationships.
5. Monetary Policy and the Federal Reserve
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/thinkstockphotos_80410231-5bfc2b97c9e77c0026b4fb20.jpg)
The Steward of Monetary Stability
The Federal Reserve, the central banking system of the USA, plays a crucial role in shaping monetary policy. Through interest rate adjustments and other measures, the Federal Reserve seeks to achieve price stability, full employment, and sustainable economic growth.
6. Entrepreneurship and Innovation

Catalysts for Economic Dynamism
Entrepreneurship and innovation are driving forces behind the USA's economic dynamism. The nation's entrepreneurial spirit, coupled with a robust ecosystem for innovation, fosters the creation of new businesses, technologies, and industries.
7. Income Inequality and Economic Challenges
Navigating Socioeconomic Disparities
While the USA's economy is marked by prosperity, challenges such as income inequality persist. Addressing these disparities is an ongoing concern, and policymakers grapple with strategies to ensure equitable economic opportunities for all segments of society.
8. Government Role in Economic Policy

Balancing Intervention and Free Markets
The federal government plays a significant role in shaping economic policy. From fiscal stimulus measures to regulatory frameworks, government interventions aim to foster economic stability and address challenges. Balancing these interventions with the principles of a free-market economy is a continuous endeavor.
9. Labor Market Dynamics

Employment Trends and Workforce Evolution
The labor market is a key component of the USA's economy. Employment trends, workforce demographics, and evolving job markets contribute to the nation's economic narrative. Technological advancements and automation are factors influencing the nature of work and skills in demand.
10. Economic Resilience and Challenges

Adapting to Change and Global Dynamics
The USA's economy has demonstrated resilience in the face of various challenges, including economic downturns and global crises. However, adapting to changing global dynamics, addressing environmental concerns, and fostering sustainable growth are ongoing imperatives.
Conclusion
The USA's economy is a multifaceted and dynamic entity that reflects the nation's historical evolution and global influence. From its agrarian roots to its position as a technological and financial powerhouse, the economic landscape of the United States is shaped by a myriad of factors. As the nation navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its economic policies and innovations continue to have a profound impact on the global stage.
In conclusion, this comprehensive guide provides a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of the USA's economy—a narrative of growth, resilience, and ongoing adaptation to the ever-changing currents of the global economic landscape.
FAQs
Q. What are the key historical foundations of the USA's economy?
Ans: The USA's economy evolved from agrarian roots to become an industrial powerhouse during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, driven by the Industrial Revolution.
Q. What are the key economic indicators used to gauge the USA's economy?
Ans: Key economic indicators include Gross Domestic Product (GDP), unemployment rates, inflation rates, and consumer spending. These indicators provide insights into economic growth, employment trends, and overall economic stability.
Q. How does the USA participate in global trade and economic partnerships?
Ans: The USA is a major player in global trade, engaging in economic partnerships with nations worldwide. Trade agreements, such as NAFTA and USMCA, shape the nation's trade policies and influence its economic relationships.
Q. What role does the Federal Reserve play in shaping the USA's economy?
Ans: The Federal Reserve, as the central banking system of the USA, plays a crucial role in shaping monetary policy. It uses tools like interest rate adjustments to achieve price stability, full employment, and sustainable economic growth.
Q. What are the challenges and ongoing concerns in the USA's economy?
Ans: Challenges include income inequality, which policymakers strive to address. Ongoing concerns involve balancing government interventions with free-market principles, adapting to labor market dynamics, and fostering sustainable growth.